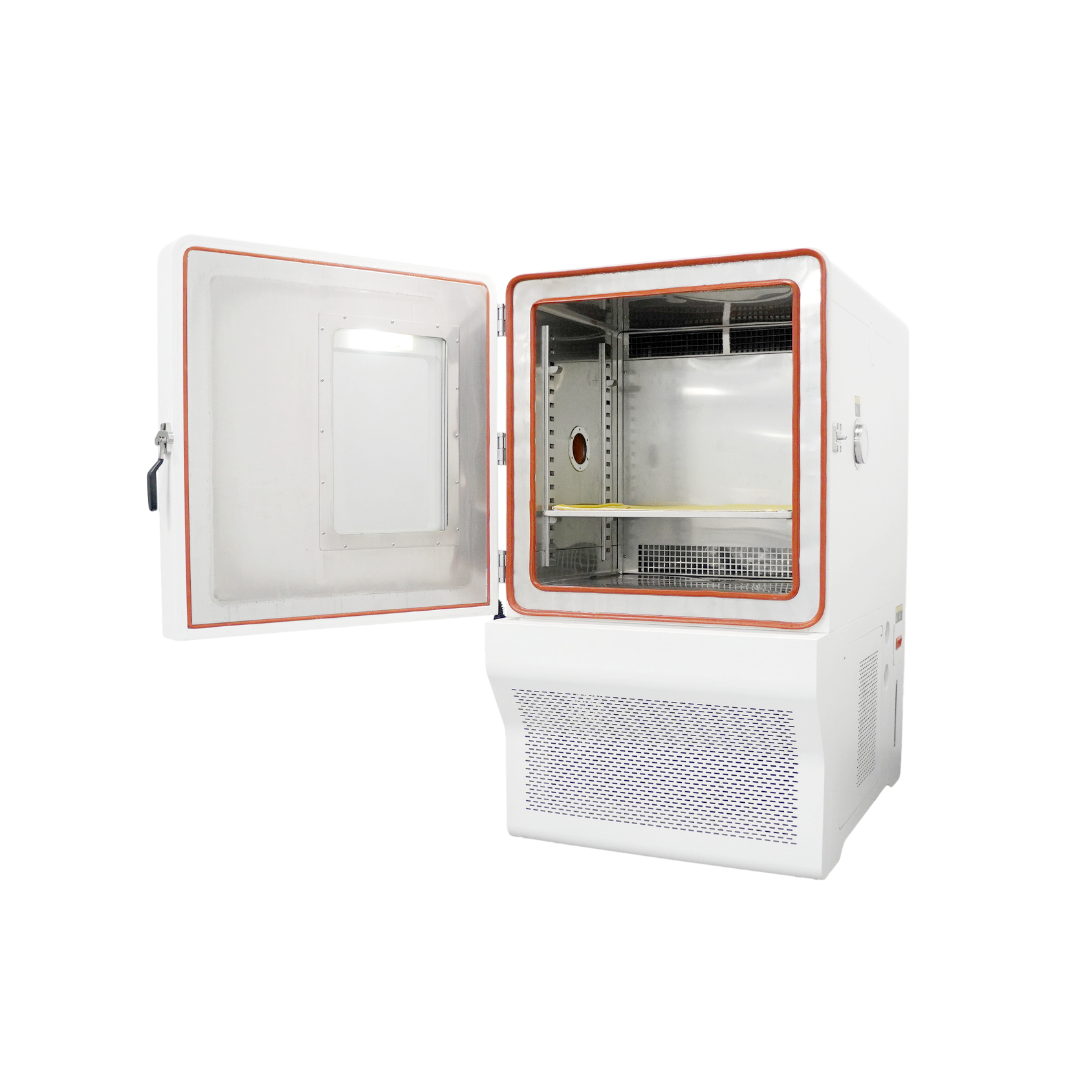
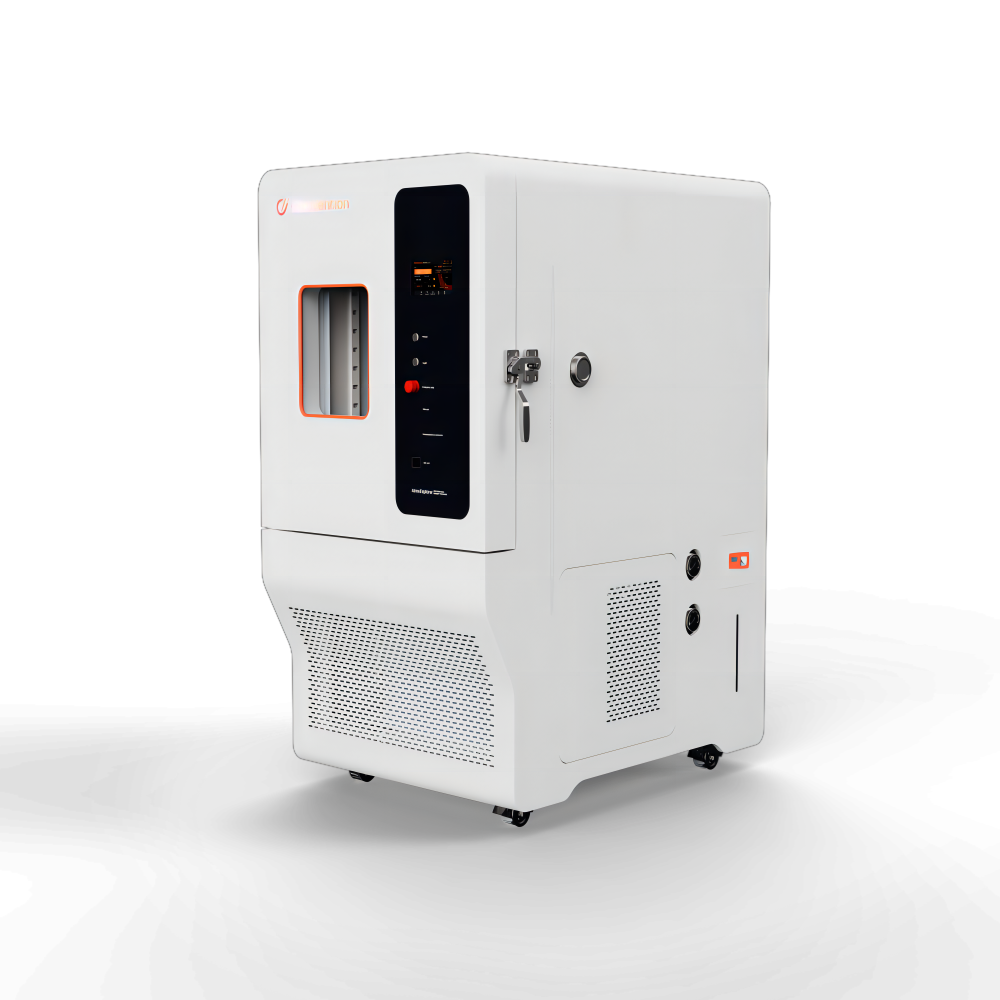
Temperature Humidity Chamber
Key Considerations for Using Constant Temperature and Humidity Chambers
Utilizing constant temperature and humidity chambers across diverse industries and materials requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Here are essential aspects to keep in mind when employing these chambers in different industrial settings or with various materials:
Temperature and Humidity Range: Understand the specific temperature and humidity requirements of the materials or processes involved in your industry.
Varied materials may have unique sensitivities to temperature and humidity, necessitating precise control within narrow ranges to prevent damage or degradation.
Material Compatibility: Consider the compatibility of the temp and humidity chambers with the materials being tested or processed. Certain materials may react adversely to specific chamber materials or environmental conditions, leading to unintended consequences such as corrosion, degradation, or contamination.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the constant temperature and humidity chamber meets relevant industry standards and regulatory requirements for your specific application or industry. Compliance with standards such as ISO, ASTM, or regulatory agencies ensures that your testing or manufacturing processes adhere to quality and safety protocols.
Sample Size and Configuration: Consider the size, shape, and configuration of the samples or materials being tested or processed within the chamber. Optimize chamber setup and layout to accommodate varying sample sizes, shapes, or quantities while ensuring uniform exposure to temperature and humidity conditions.
Testing Protocols and Procedures: Develop and adhere to standardized testing protocols and procedures tailored to your industry or material requirements. Establish clear guidelines for sample preparation, testing duration, data collection, and analysis to ensure consistency and reproducibility of results across different testing scenarios.
Monitoring and Control Systems: Implement robust monitoring and control systems within the temp and humidity chambers to track and maintain desired environmental conditions accurately. Utilize advanced sensors, data loggers, and automated control algorithms to ensure precise control and real-time monitoring of chamber parameters.
Calibration and Maintenance: Regularly calibrate and maintain the constant temp and humidity chambers to ensure accurate performance and reliability over time. Schedule routine maintenance checks, calibration procedures, and quality assurance measures to identify and address any deviations or malfunctions promptly.
Material Handling and Safety: Establish proper material handling procedures and safety protocols to minimize risks associated with the operation of constant temp and humidity chambers. Ensure adequate ventilation, safety interlocks, and emergency shutdown procedures to protect personnel and equipment from potential hazards.
Data Management and Documentation: Implement robust data management and documentation practices to record and archive testing or manufacturing data generated within the constant temperature and humidity chamber. Maintain detailed records of experimental conditions, sample characteristics, and test results for traceability, analysis, and future reference.
Adaptability and Flexibility: Design constant temperature and humidity chamber setups that offer adaptability and flexibility to accommodate changing industry requirements, materials, or testing protocols. Invest in modular chamber configurations, interchangeable accessories, or software updates to future-proof your testing or manufacturing capabilities.
Ensuring Reliability in Constant Temperature and Humidity Chamber Tests
Achieving reliable test results in constant temp and humidity chambers is paramount for making informed decisions in various industries and applications. Here are essential strategies to enhance the reliability of tests conducted within these chambers:
Calibration and Validation: Regularly calibrate and validate the constant temperature and humidity chamber to ensure accurate and consistent performance. Use traceable standards and procedures to verify temperature and humidity sensors, controllers, and other critical components.
Standardized Procedures: Develop standardized testing procedures and protocols tailored to your specific industry or application. Clearly define test parameters, sample preparation methods, testing durations, and data collection protocols to ensure consistency and reproducibility of results.
Sample Preparation: Follow meticulous sample preparation procedures to minimize variability and ensure uniformity across test specimens. Standardize sample size, shape, orientation, and placement within the chamber to reduce experimental errors and enhance the comparability of results.
Environmental Monitoring: Implement robust environmental monitoring systems within the chamber to track temperature and humidity conditions accurately. Utilize calibrated sensors, data loggers, and automated control algorithms to maintain desired environmental setpoints and detect deviations promptly.
Quality Control Checks: Incorporate quality control checks throughout the testing process to identify and mitigate potential sources of error or variability. Conduct periodic checks of chamber performance, sample integrity, and data consistency to maintain confidence in test results.
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Employ rigorous data analysis and interpretation techniques to extract meaningful insights from test results. Use statistical methods, trend analysis, and data visualization tools to identify patterns, outliers, or trends that may influence the reliability of test outcomes.
Peer Review and Collaboration: Foster a culture of peer review and collaboration within your organization or research community to validate test methodologies, share best practices, and ensure the robustness of experimental designs. Solicit feedback from colleagues, experts, or external stakeholders to improve the reliability of tests conducted in constant temperature and humidity chambers.
Documentation and Reporting: Maintain detailed documentation of test procedures, experimental conditions, sample characteristics, and results in comprehensive test reports. Document any deviations, anomalies, or unexpected observations encountered during testing to facilitate troubleshooting and future analysis.
Risk Management: Identify and mitigate potential sources of risk or uncertainty that may impact the reliability of test results. Conduct risk assessments to identify critical control points, failure modes, and mitigation strategies to minimize the likelihood of errors or biases in test outcomes.
Continuous Improvement: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement to enhance the reliability of tests conducted in constant temperature and humidity chambers. Solicit feedback from stakeholders, monitor performance metrics, and implement corrective actions or process improvements to optimize testing practices over time.
Sign up for advice
- Hotline0902 596 388
- emailsale1@amitec.com.vn